Each time you click on content in the web browser panel, Content Grabber does some processing in the background to calculate the selection XPath. XPath is a common syntax for selecting in XML and HTML documents. Content Grabber uses a standard implementation that supports XPath v1.0 syntax, and also supports a range of new methods specifically designed to make web scraping easier. Content Grabber has a range of tools that helps you create a precise XPath, without the need to know the syntax. Eventually, you may find the need to fine-tune the XPath manually, and then you will need to learn the XPath syntax.
Each time you make a selection in the web browser, you can view the selection XPath either in the XPath panel or on the status bar (see the figures below).
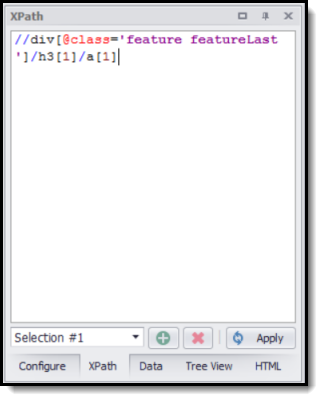
The selection XPath panel
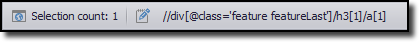
The selection XPath is shown on the status bar
The XPath in the figure above is:
//div[@class='feature featureLast']/h3[1]/a[1]
It contains these selection steps:
1.Selects all <div> tags within the webpage having the class attribute value feature featureLast.
2.Also selects all child <h3> tags from the selection in step 1 (/h3[1]).
3.Then selects all child <a> tags from the selection in step 2 (/a[1]).
Read more in the XPath and Selection Techniques article. To learn more about XPath, we recommend that you consult a good reference guide such as this one:
www.w3schools.com/XPath/xpath_syntax.asp
Multiple XPaths
A selection can consist of multiple XPaths. This is useful when trying to select web content that can appear in different locations on a web page.
To add an XPath to a selection, use the Add button in the XPath window. If you have multiple XPaths in a selection, you can select View All from the drop down box to view all the web content selected by all the XPaths.
Content Grabber XPath Functions
Content Grabber has a set of non-standard functions you can use in XPath selections:
Function |
Description |
bool equals(string source, string target) |
Returns True if the two strings are equal. The comparison is case insensitive. |
bool fuzzy-match(string source, string target, [double tolerance]) |
Uses the Jaro/Winkler distance algorithm to determine if two strings match. This function first splits each string into words and then compares words from each string. If one string contains more words than the other string, the additional words are not considered when calculating the distance.
Tolerance must be between 0 and 1. A tolerance of 1 means an exact match. A tolerance of 0.85 is used if tolerance is not specified. |
bool fuzzy-match(string source, string target, double singleWordTolerance, int wordMismatchesAllowed, [bool isMatchAllSourceWords], [bool isMatchAllTargetWords]) |
Uses the Jaro/Winkler distance algorithm to determine if two strings match. This function first splits each string into words and then compares words from each string.
If isMatchAllSourceWords is true, all words in the source string will be matches.
If isMatchAllTargetWords is true, all words in the target string will be matches.
if both isMatchAllSourceWords and isMatchAllTargetWords are true, all words in the string containing the most words will be matched.
if both isMatchAllSourceWords and isMatchAllTargetWords are false, all words in the string containing the least words will be matched.
SingleWordTolerance must be between 0 and 1. A tolerance of 1 means an exact match. If a word match is less than the SingleWordTolerance value, a word mismatch is recorded.
WordMismatchesAllowed is the number of words that are allowed to mismatch before the function returns false. |
bool not-whitespace(string source) |
Returns False if the string contains only white space characters. |
add-bookmark() |
Adds the current node to an internal list of bookmarks. |
bool has-parent-bookmark() |
Returns True if a parent of the current node is in the bookmark list. |
NodeSet parent-bookmark() |
Returns the first parent node that is in the bookmark list. |
string html() |
Returns the HTML of the current node. |
string inner-html() |
Returns the inner HTML of the current node. |
string uniqueid() |
Returns a unique ID. |
string url() |
Returns any URL property of the current node. |
string image-url() |
Returns any image URL of the current node. |
string email() |
Returns any email address of the current node. |
string flash-url() |
Returns any flash URL of the current node. |
string tag-text() |
Returns the text of the current node excluding text from any child nodes. |
string find-data(string commandName) |
Returns the extracted data for a command that has already been processed. If the command does not exist in the current container command, the function will keep searching in parent containers. |
string get-data(string commandName) |
Returns the extracted data for a command that has already been processed. The command must exist in the current container command. |
string get-input-data(string commandName, string columnName) |
Returns input data as a string value from the specified data column in the data provided by the specified command. The specified command must be a data provider. |
string get-input-data(string columnName) |
Returns input data as a string value from the specified data column in the data provided by the last data provider parent command. |
string get-input-data() |
Returns input data from the first data column that contains a string value in the data provided by the last data provider parent command. |
string get-global-data(string name) |
Returns the data entry with the specified name from the global data dictionary which includes input parameters. The data entry must be a string value or a simple value type that can be converted to a string value. |
int node-position([nodeSet]) |
Returns the position of a specific node among all nodes with the same parent node. If no node is given, then this is the position of the root node.
When choosing elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So a call to node-position() would return the position of the current list element.
The index is not zero based, so the first index is 1. |
NodeSet root([int nodeIndex]) |
Returns the root node with a specific index. The index must be greater than 1. If no index is specified the current root node is returned.
When selecting elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So, a call to root() would return the current list element, and a call to root(2) would return the second list element. |
int root-index() |
Returns the index of the current root node.
When selecting elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So, a call to root-index() would return the index of the current list element.
The index is not zero based, so the first index is 1. |
int last-root-index() |
Returns the index of the last root node.
When selecting elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So, a call to last-root-index() would return the index of the last list element.
The index is not zero based, so the first index is 1. |
int root-position() |
Returns the position of the current root node. This position is relative to all nodes with the same parent node.
When selecting elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So, a call to root-position() would return the position of the current list element.
The index is not zero based, so the first index is 1. |
NodeSet root-siblings() |
Returns following siblings of the current root node, but stops when it encounters another root node.
This function is equivalent to the following selection:
root()/following-sibling::*[root-index()=last-root-index()
or
position()<root-position(root-index()+1)-root-position()]
When selecting elements inside a web element list, the current list element is the root node. So, a call to root-siblings() would return siblings of the current list element. |